I've been working on a project where the requirement was to send emails via Amazon SES and track deliverability status with webhooks. Not surprisingly, at least for me, the ride wasn't a smooth one. You see, I have a love & hate relationship with AWS. Thanks to Krishankant Singhal's articles on Amazon SES and Laravel Implementation I managed to get through, however, there were some pieces of the puzzle that I would like to cover and help you avoid spending hours searching for those missing pieces.
Let's start with Laravel's code.
Is straight forward. See Laravel Docs
Make sure all those env variables are set. We will use AWS_SES_CONFIGURATION_SET_NAME later when we are setting up the configuration set. You can name it however you want.
// .env
MAIL_MAILER=ses
MAIL_FROM_ADDRESS=
MAIL_FROM_NAME=
AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID=
AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY=
AWS_DEFAULT_REGION=
AWS_BUCKET=
AWS_SES_CONFIGURATION_SET_NAME=bounces
Make sure to add withSwiftMessage when building email; otherwise, things won't work. You can thank me later :). I lost hours here.
Without x-ses-configuration-set webhook won't be triggered. unique-id header is used to keep tracking emails.
->withSwiftMessage(function ($message) use ($uuid) {
$message->getHeaders()->addTextHeader('x-ses-configuration-set', config('services.ses.configuration_set'));
$message->getHeaders()->addTextHeader('unique-id', $uuid);
})
<?php
// app/notifications/WelcomeNotification.php
namespace App\Notifications;
use Illuminate\Bus\Queueable;
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Log;
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\URL;
use Illuminate\Notifications\Notification;
use Illuminate\Notifications\Messages\MailMessage;
class WelcomeNotification extends Notification
{
use Queueable;
public $uniqueId;
public function __construct($validationRequest, $socialWorkerFirstName, $socialWorkerSurname)
{
$this->uniqueId = 'some random id';
}
/**
* Get the notification's delivery channels.
*
* @param mixed $notifiable
*
* @return array
*/
public function via($notifiable)
{
return ['mail'];
}
/**
* Get the mail representation of the notification.
*
* @param mixed $notifiable
*
* @return \Illuminate\Notifications\Messages\MailMessage
*/
public function toMail($notifiable)
{
$uniqueId = $this->uniqueId;
return (new MailMessage())
->withSwiftMessage(function ($message) use ($uniqueId) {
$message->getHeaders()->addTextHeader('x-ses-configuration-set', config('services.ses.configuration_set'));
$message->getHeaders()->addTextHeader('unique-id', $uniqueId);
})
->subject("Welcome")
->greeting("Welcome")
->line("Welcome")
->action("Login", url('/'));
}
}
I won't spend too much time here. See Laravel Docs how to do it.
// database/migrations/2019_03_13_163943_create_notification_logs_table.php
<?php
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Schema;
use Illuminate\Database\Schema\Blueprint;
use Illuminate\Database\Migrations\Migration;
class CreateNotificationLogsTable extends Migration
{
/**
* Run the migrations.
*
* @return void
*/
public function up()
{
Schema::create('notification_logs', function (Blueprint $table) {
$table->bigIncrements('id');
$table->text('status')->nullable();
$table->string('message_id');
$table->timestamps();
});
}
}
// app/NotificationLog.php
<?php
namespace App;
use Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Model;
class NotificationLog extends Model
{
protected $guarded = [];
}
See Laravel Docs how to do it. We will utilize NotificationSent event to save notification in the DB.
// app/Providers/EventServiceProvider.php
/**
* The event listener mappings for the application.
*
* @var array
*/
protected $listen = [
'Illuminate\Notifications\Events\NotificationSent' => [
'App\Listeners\LogNotification',
],
];
// app/Listeners/LogNotification.php
<?php
namespace App\Listeners;
use Illuminate\Notifications\Events\NotificationSent;
use App\NotificationLog;
class LogNotification
{
/**
* Handle the event.
*
* @return void
*/
public function handle(NotificationSent $event)
{
$notification = $event->notification->uniqueId;
NotificationLog::create([
'message_id' => $event->notification->uniqueId,
'status' = null
]);
}
}
Last but not least, we need an endpoint that Amazon can post to email delivery status updates.
Install aws packages
composer require aws/aws-php-sns-message-validator
composer require aws/AWS-SDK-PHP
Create controller
// app/Http/Controllers/SnSController.php
<?php
namespace App\Http\Controllers;
use Aws\Sns\Message;
use Aws\Sns\MessageValidator;
use Illuminate\Http\Response;
use App\Models\NotificationLog;
use App\Http\Controllers\Controller;
use Aws\Sns\Exception\InvalidSnsMessageException;
class SnsController extends Controller
{
public function store()
{
// Only needed first time to get the subscription url to confirm the webhook
// Log::info(file_get_contents('php://input'));
$message = Message::fromRawPostData();
$validator = new MessageValidator();
try {
$validator->validate($message);
} catch (InvalidSnsMessageException $e) {
Log::error('SNS Message Validation Error: '.$e->getMessage());
}
$messageBody = json_decode($message->offsetGet('Message'), true);
$uniqueId = $this->getUniqueIdFromHeader($messageBody);
$notificationLog = NotificationLog::where('message_id', $uniqueId)->first();
if ($notificationLog === null) {
return response()->json([], Response::HTTP_OK);
}
$notificationLog->update([
'status' => $messageBody['eventType'],
]);
return response()->json([], Response::HTTP_OK);
}
private function getUniqueIdFromHeader($messageBody)
{
return collect($messageBody['mail']['headers'])->filter(function ($header) {
return $header['name'] === 'unique-id';
})->map(function ($header) {
return $header['value'];
})->first();
}
}
Create Route
// routes/web.php
Route::post('/webhooks/sns', [App\Http\Controllers\SnsController::class, 'store']);
Phew, we are done with Laravel.
Sorry, I can't help you here. In my case, SES was already in place. However, I've done the heavy lifting for you and googled this article Sending email in Laravel using SMTP and Amazon SES for you.
 Login to AWS console and type
Login to AWS console and type sns in the search bar and select Simple Notification Service.
 In the navigation click on
In the navigation click on Topics and then on the right side click on the button Create Topic.
 Select
Select Standard type and give it a name. Save it.
Remember to uncomment Log::info(file_get_contents('php://input')) in SnsController before creating new topic's subscription
// Only needed first time to get the subscription url to confirm the webhook
// Log::info(file_get_contents('php://input'));
from SnsController. You should uncomment this before subscription is created.
 On newly created topic's page click on the button
On newly created topic's page click on the button Create Subscription.
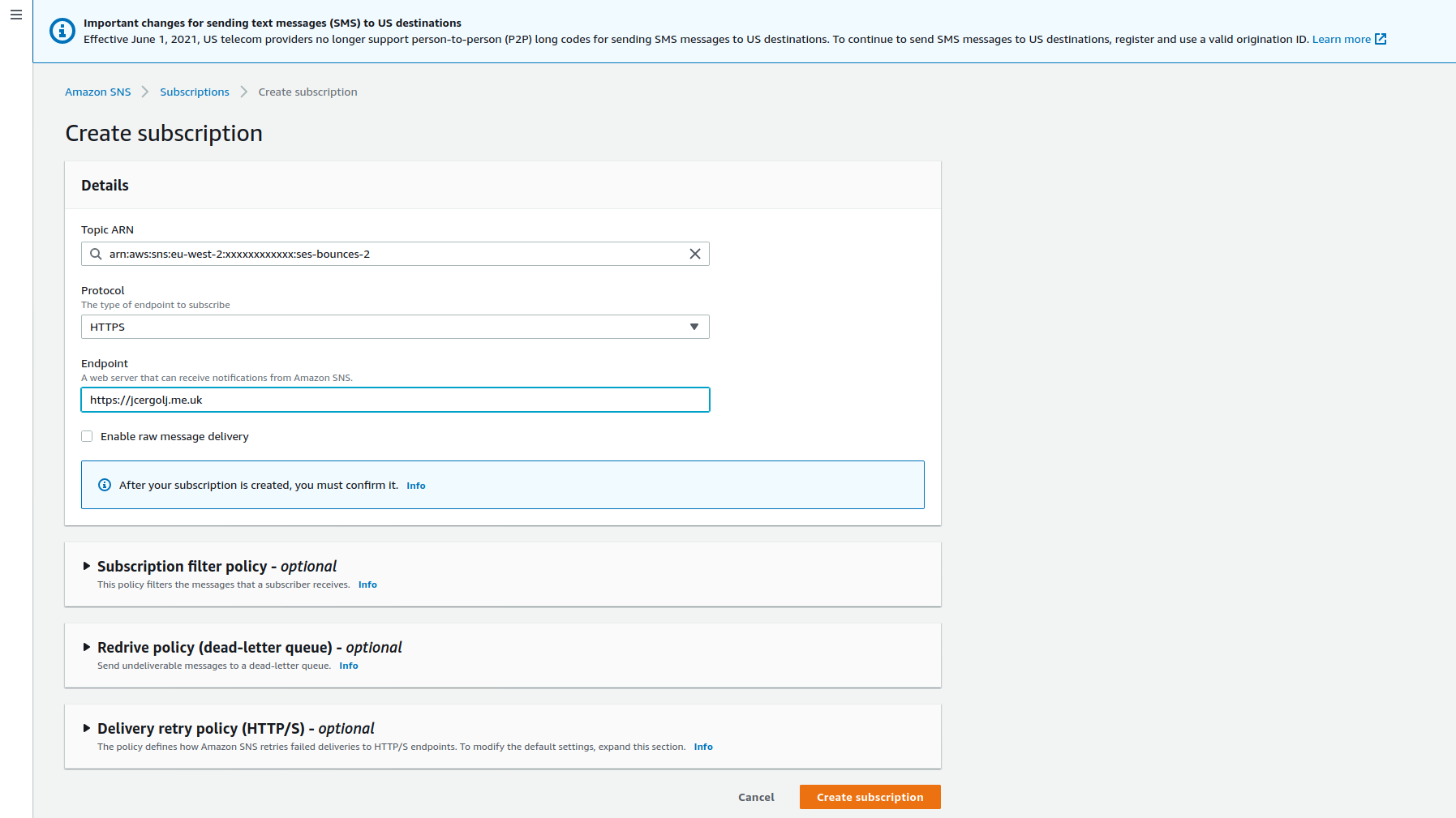 Create new subscription. Topic ARN must match the previously created one. Select
Create new subscription. Topic ARN must match the previously created one. Select https protocol and define endpoint. Save.
 Select created subscription and click on
Select created subscription and click on Confirm Subscription.
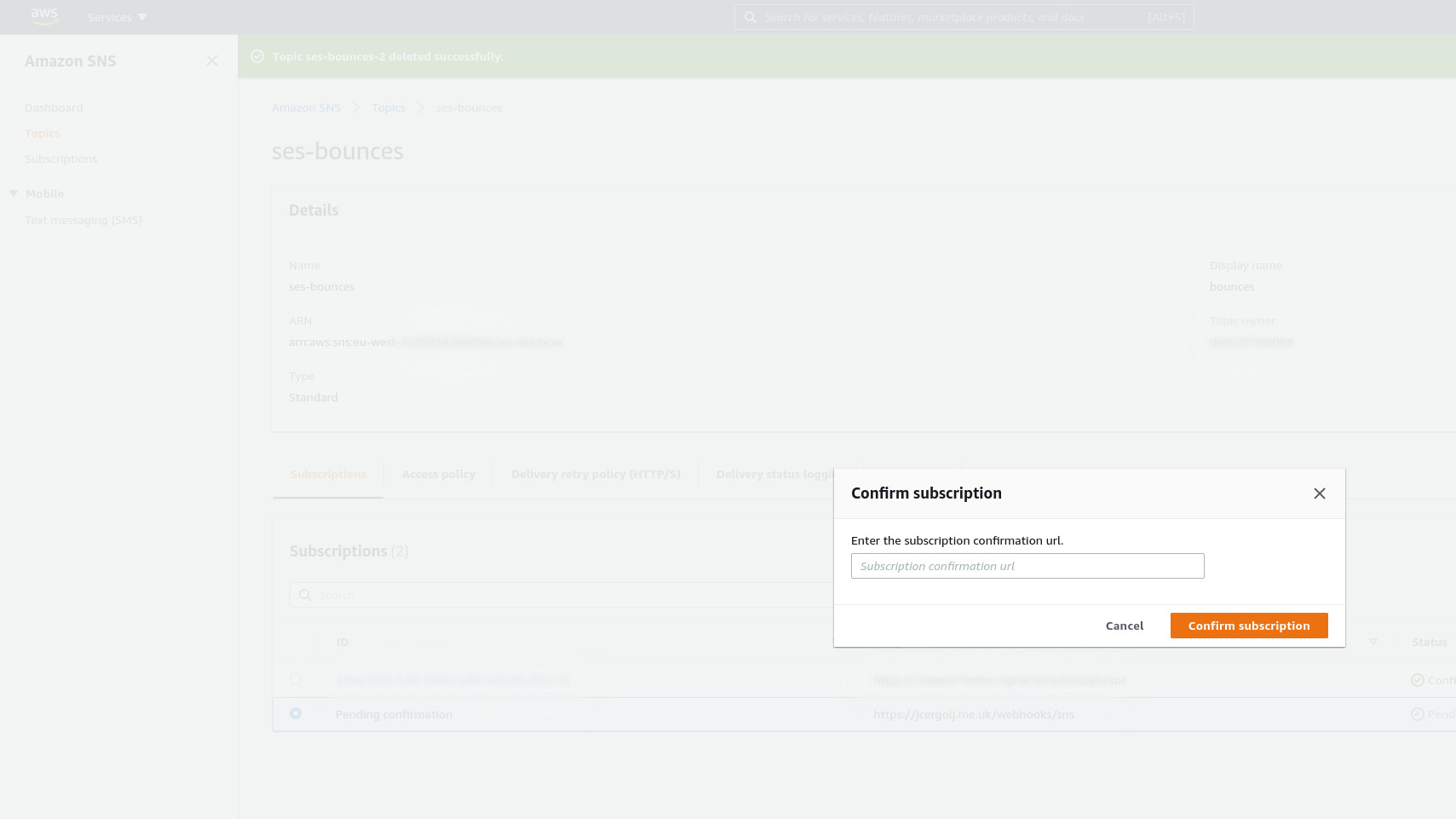 Locate subscription url in the log file and paste it here.
Locate subscription url in the log file and paste it here.
 Type
Type ses in the search bar and select Amazon Simple Email Service.
 In the left nav click on 'Configuration Sets.
In the left nav click on 'Configuration Sets.
 In the left nav click on 'Configuration Sets.
In the left nav click on 'Configuration Sets.
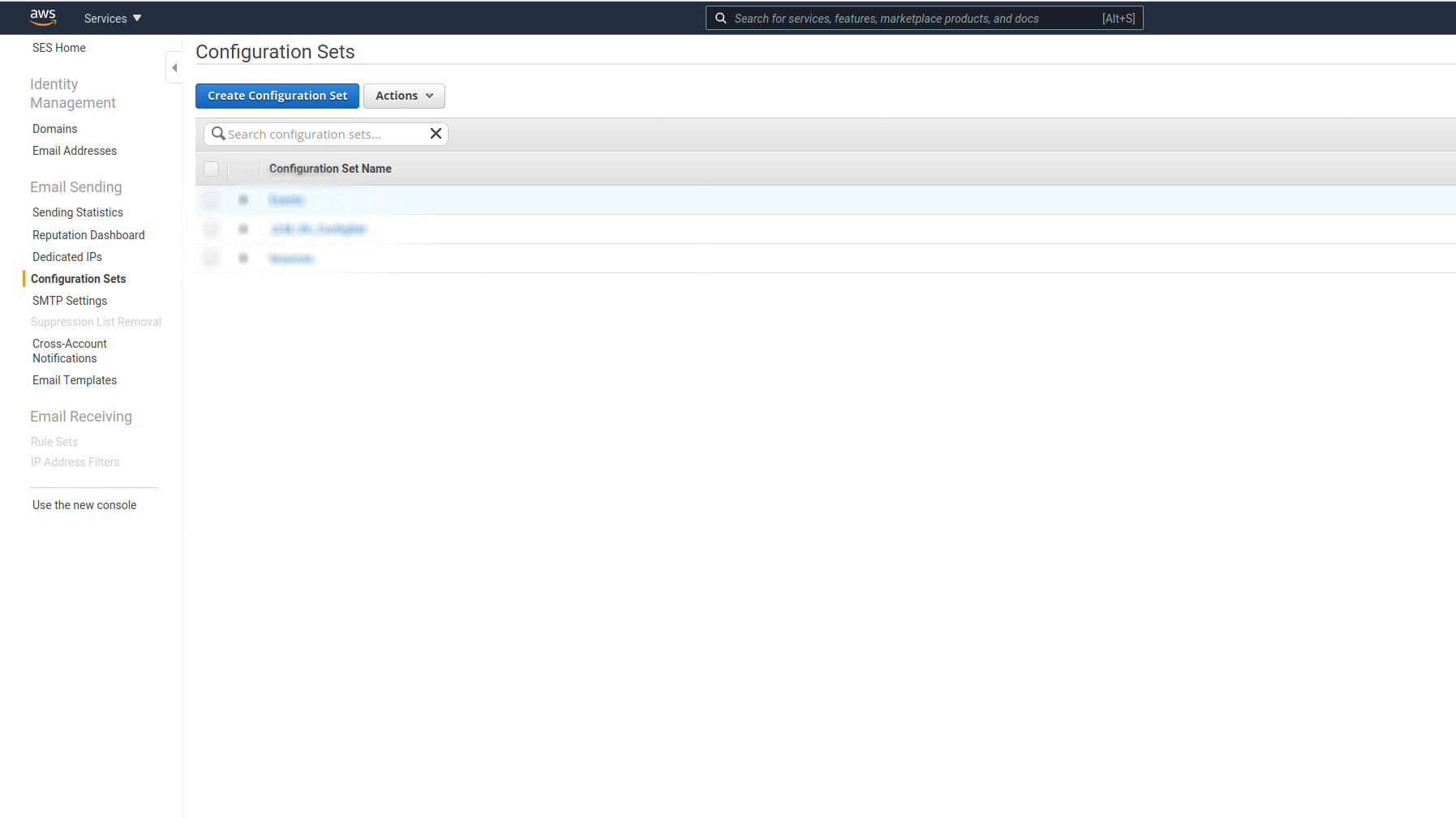 Click on the button
Click on the button Create New Configuration Set.
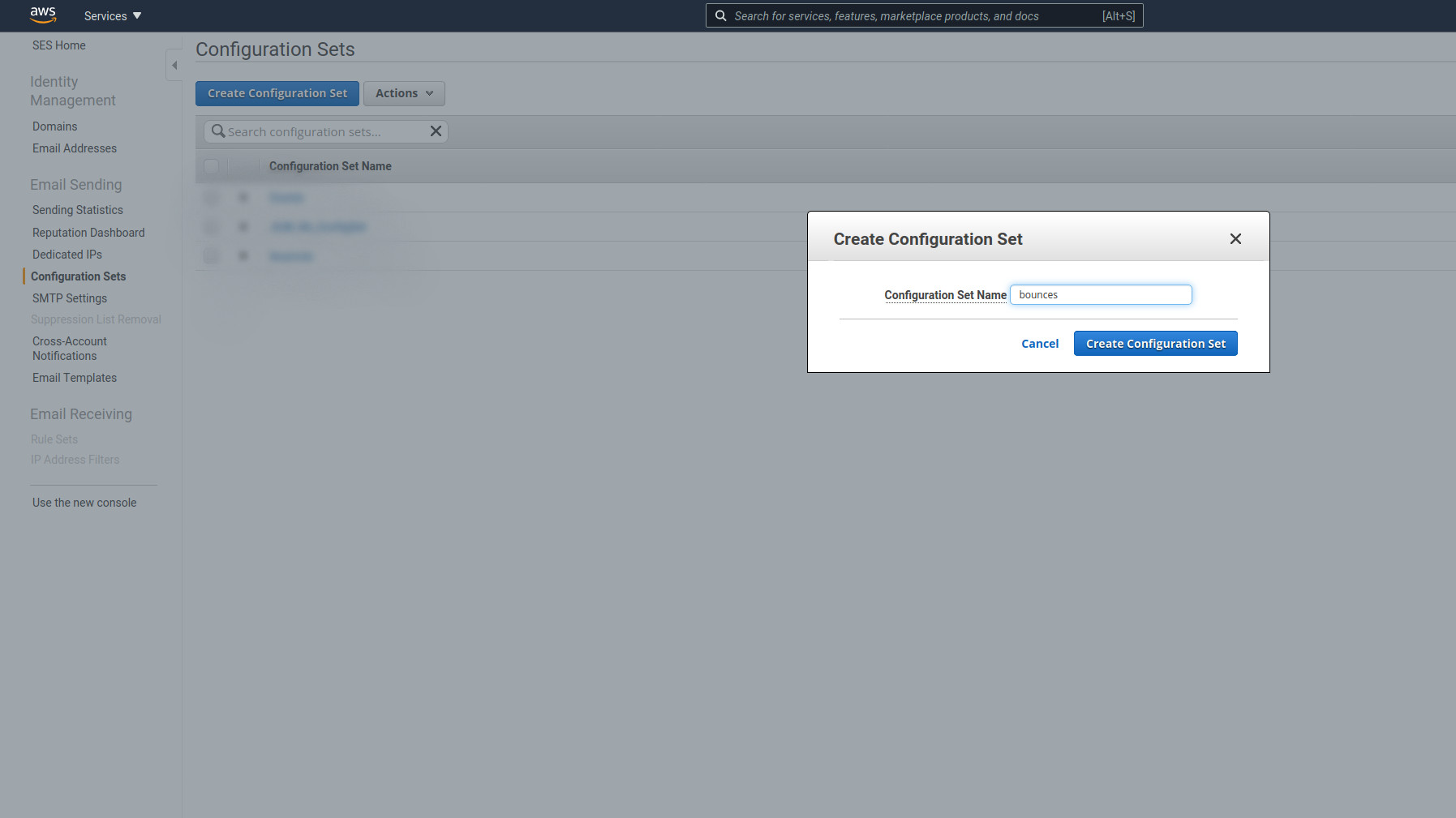 Give it a name. Must be the same as .env
Give it a name. Must be the same as .env AWS_SES_CONFIGURATION_SET_NAME=bounces variable.
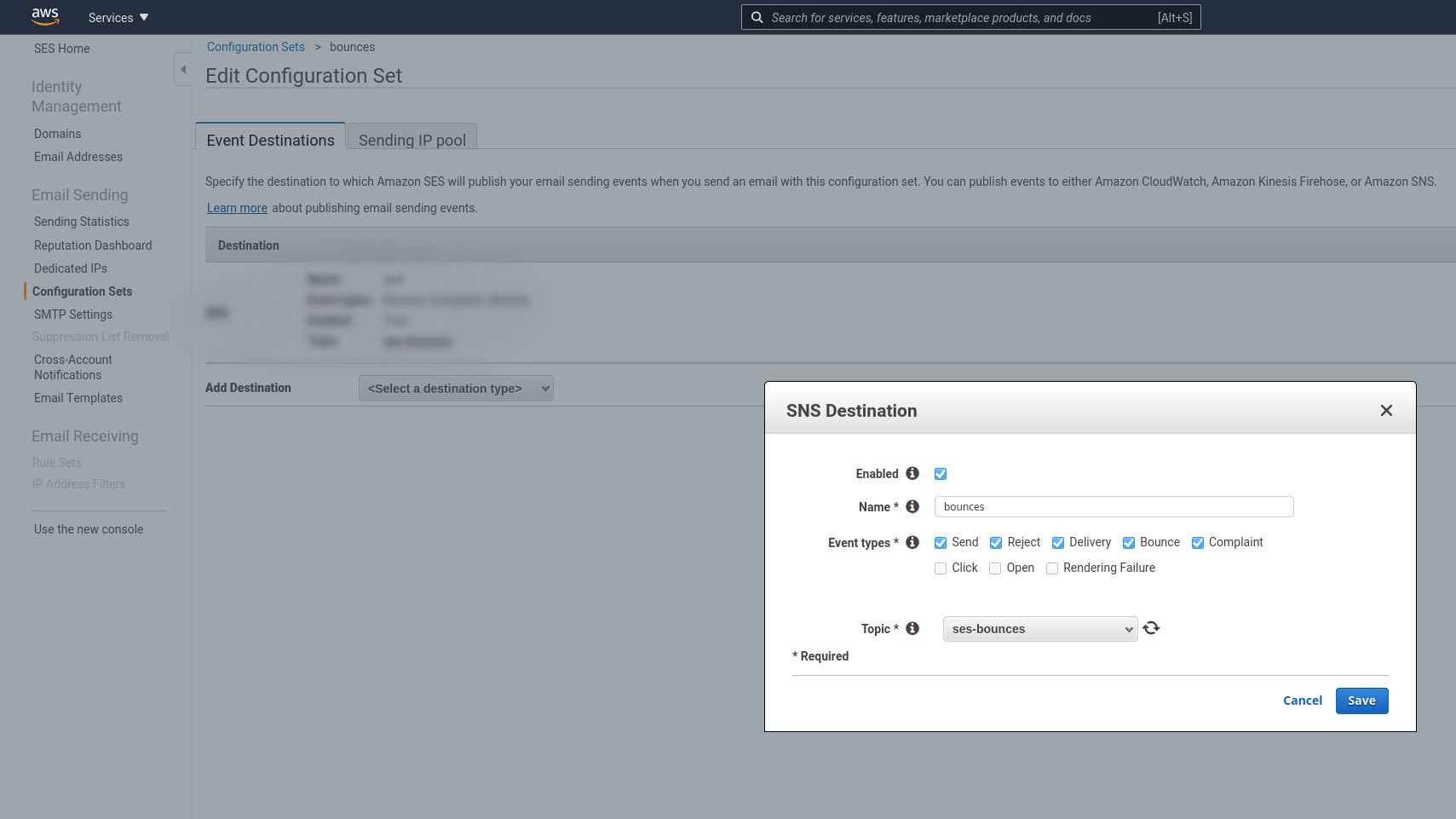 Fill the form with name, sns topic and event types.
Fill the form with name, sns topic and event types.
And you are done.
Hopefully, this somehow lengthy tutorial makes sense, and that helped you save hours of your precious time. I wasn't so lucky.